Software

Our advanced data analysis program, FargoFit, meets highest standards in precision and
speed of fluorescence lifetime data fitting. It is designed to globally analyze hundreds of
time-resolved luminescence waveforms by least-square minimization, using a wide range of fitting
models, which can include exponential decays, quenching, fluorescence resonance energy transfer,
excited-state reactions, rotational diffusion, and transient chemical reactions. The iterative
reconvolution algorithm is used to account for the finite Instrument Response Function (IRF).
During the global analysis some fit parameters can be linked, i.e. they remain free-floating,
but they are identical in all linked waveforms. It is the ideal solution for analysis data of
time-resolved FRET and double kinetic experiments.
The program requires Microsoft .NET Framework 4.0 or newer. Latest version of the program can
be downloaded from the Downloads page. Program is free and is
provided "AS IS".
Current version of the program is:
3.16.0.0
(What is new?)
Key features
- Marquardt and Simplex minimization algorithms.
- Rigorous error analysis using Support-Plane method.
- The program supports data files from Double Kinetic Systems instruments,
Becker-Hickl .sdt files, and plain text ASCII data files.
- Virtually unlimited number of waveforms and data points.
- The software is available for Windows XP/Vista/7 and features a modern and easy to use
graphical user interface.
- Fitting function is constructed using graphical user interface by combining different
relaxation processes in the decay model.
- There are several original components introduced in fitting function
like fractions of interacting components, relative amplitude of different waveforms, etc.
- Modeling of stopped-flow kinetics and other double-kinetic processes by including kinetic
of fractions in fitting function.
- Extensive parameters linking capabilities.
- Scripting language for automatization of model creation and parameter linking.
- The fitting limits are easily adjusted with graphical sliders.
- Easy to navigate through spectra and transient kinetics series.
- Data simulation.
- Simplified data handling - .ff file format stores data and analyses in one file.
Case studies
Coumarin 540A
Rose Bengal
Anthracene
Decay Associated Spectra
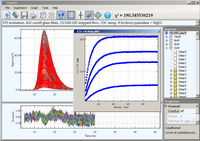
Mg-Quinoline chelate formation 1
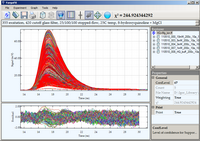
Mg-Quinoline chelate formation 2

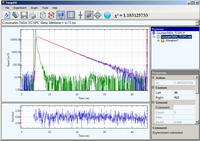
Luminescence decay of Coumarin 540A acquired using Time Correlated Single Photon Counting.
The 405 nm laser diode was used for excitation. The emission was collected through a 430 nm
long-pass filter and emission polarizer oriented at magic angle (54.7
o). The data
is best fitted by a single exponential decay with lifetime 4.72 ns.

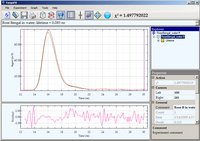
Luminescence decay of Rose Bengal in water acquired by direct waveform recording.
The 2
rd harmonic of YAG laser (532 nm) was used for excitation.
The emission was collected through a 550 nm long-pass filter
and emission polarizer oriented at magic angle (54.7
o) The data is best fitted
by a single exponential decay with lifetime 0.085 ns.

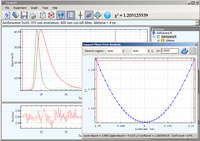
Luminescence decay of Anthracene in Methanol acquired by direct waveform recording.
The 3
rd harmonic of YAG laser (335 nm) was used for excitation. The emission
was collected through a 400 nm long-pass filter and emission polarizer oriented at magic
angle (54.7
o). The data is best fitted by a single exponential decay with
lifetime 4 ns. Confidence interval of lifetime parameter is determined by support
plane error analysis as 3.99 – 4.01 ns.
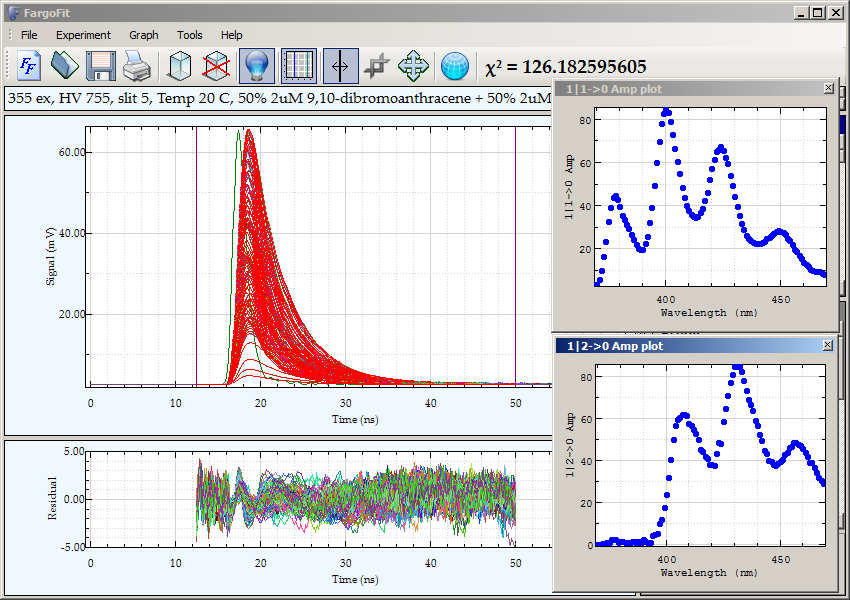
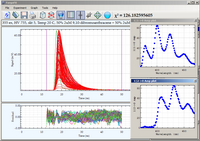
Luminescence decays of the mixture of anthracene and 9,10-dibromoanthracene acquired by direct waveform recording.
The 3
rd harmonic
of YAG laser (355 nm) was used for excitation. The emission wavelength was scanned from 370 to 470 nm with a 1-nm step size.
The data is best fitted by a double exponential decay with both lifetimes linked across waveforms. The recovered
lifetimes are 3.95 ns for anthracene and 1.2 ns for 9,10-dibromoanthracene. Plots of pre-exponential factors
vs. emission wavelength correspond to contours of steady-state emission spectra of components in mixture.

Four series of 200 luminescence decays were acquired in a stopped-flow apparatus using Double-Kinetic approach
after mixing MgCl
2 and 8-hydroxyquinoline solutions for 5 concentrations of MgCl
2.
Concentration of MgCl
2 was at least 10 times that of 8-hydroxyquinoline to maintain pseudo-first-order
reaction conditions. Third harmonic of YAG laser (335 nm) was
used for excitation. The emission was collected through a 420 nm long-pass filter and emission polarizer oriented
at magic angle (54.7
o). All these data (400,000 data points) were globally analyzed using single-exponent
model with lifetimes liked across all waveforms.

Five series of 200 luminescence decays were acquired in a stopped-flow apparatus using Double-Kinetic approach
after mixing MgCl
2 and 8-hydroxyquinoline solutions for 5 concentrations of MgCl
2.
Concentration of MgCl
2 was at least 10 times that of 8-hydroxyquinoline to maintain pseudo-first-order
reaction conditions. Third harmonic of YAG laser (335 nm) was
used for excitation. The emission was collected through a 420 nm long-pass filter and emission polarizer oriented
at magic angle (54.7
o). All these data (500,000 data points) were globally analyzed and the following
parameters were recovered from single-step analysis: luminescence lifetimes of 8-hydroxyquinoline and Mg-Quinoline
complex, associate and dissociate rate constants, and dead time of mixing apparatus.
For more details please contact us.